The International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) is a professional association that was incorporated in 1985 for the trading of swaps and derivatives. ISDA was created as many financial institutions faced challenges on account of the increased use of derivatives & also due to the lack of risk clarity the parties to the transaction would face.
ISDA Master Agreement is a standard contract to govern all over-the-counter (OTC) derivative transactions entered between the parties. OTC derivatives are mainly used for hedging purposes. For example, there is an adverse movement in the market and a company expects floating interest rates to increase, therefore, it can enter an interest rate swap to lock in the fixed interest rate for a specific period.
ISDA master agreement also applies to future agreements i.e. the parties to the contract don’t have to renegotiate the terms every time they enter into any transaction, thereby saving the legal cost. It includes all terms and conditions including definitions and the terms for future transactions, but they can always add or modify any new clause to the agreement by using the ISDA schedule.
Book your CFADemo Session Click Here
There are two versions of the ISDA master agreement, ‘ISDA Master Agreement 1992’ and ‘ISDA Master Agreement 2002’. ISDA Master Agreement 1992 uses Market Quotation/ Loss Method in which parties to the agreement consider an average of quotations from leading swap market dealers and based on that they agree upon a fair compensation for early termination and ISDA Master Agreement 2002 uses close out method in which parties to the agreement decide fair compensation.
The ISDA master agreement includes five main themes such as Events, Close-out and Netting, Disputes, Payment and deliveries, Contract Formation, and Legal Relations.
I. Events
Event of default
An event of default is an act where one party to an agreement is at fault also known as a defaulting party. Some of the examples may include failure to perform a transaction i.e. to pay or deliver, breach of agreement i.e. non-delivery of specific information, insolvency, etc.
Termination events
When the contract has been terminated much earlier than the original contract period it is known as termination event. Unlike events of default, in this scenario, no parties to the contract are at fault. Some of the examples are illegality (if it is unlawful for a party to make or receive any payment), force majeure (natural disasters, man-made catastrophes, an act of terrorism), tax event (changes in law because of which tax has been imposed on a transaction), credit event upon merger (wherein the creditworthiness of a party has been deteriorated).
II. Close-out and netting
ISDA Master Agreement contains a provision that allows a party to terminate a transaction in case of an event of default or termination event and contains a procedure through which only the net amount is derived and a single amount is produced which is payable between the parties.
For Example: As we can see in the diagram below transaction is between Party A (non-defaulting party) and Party B (defaulting party). Party A has to pay $1,000,000 and Party B has to pay $800,000. Under the netting agreement, Party A has to pay only the net amount i.e. $ 200,000. In the case where close-out netting is not considered Party A has to pay the full amount of $1,000,000 but the recovery amount from Party B may be less than $800,000 in case party B becomes bankrupt.
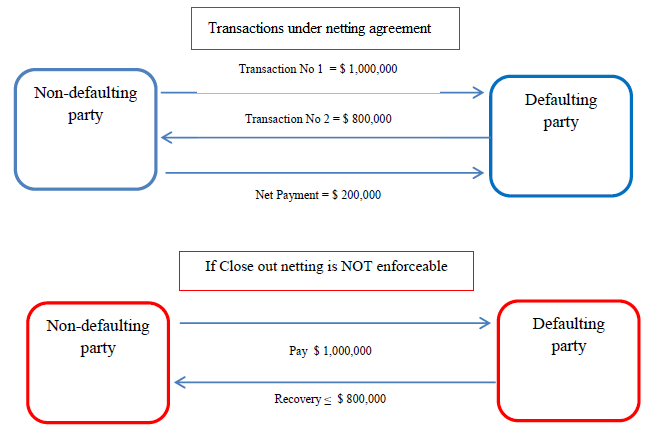
In case of bankruptcy, close-out netting concept helps the non-defaulting party by preventing a liquidator from cherry-picking i.e. choosing to make payments on transactions that are profitable to his bankrupt client (in this case Party B) and not focusing on unprofitable ones.
Book your FRM Demo Session Click Here
III. Payments and deliveries
As per the ISDA Master Agreement, the parties to an agreement should always make a payment to each other as and when due. There are provisions which affect the quantum and how the payments are made. The payments will be made in the currency agreed upon by the parties
If an event of default or termination event occurred with one of the parties, then the other party is not obliged to make a payment until the event continues. Therefore, it means during the duration of an event payment is suspended.
IV. Disputes
Disputes can arise between the parties during a transaction and the ISDA Master Agreement sets a manner in which dispute can be resolved.
V. Contract Formation and Legal relations
Apart from the other provisions mentioned above, there are other provisions like agreement contains various obligations which must be adhered to through the duration of the agreement, each party to act as a principal and not as an agent to any person or entity, transfer of rights and obligations to another party, the provisions relating to amendments.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the ISDA agreement is a boon for parties trading in OTC market derivatives.
Author: Swati Krishnamurthy
About the Author:
Swati is a freelance writer. She is a Financial Quality Compliance specialist having integrated knowledge and experience in Logistics, Audit, and Risk-mitigation for manufacturing and service sectors. Her passion for finance grew as she scored centum in financial management during her master’s degree. She’s a classical dancer who performs to express complex emotions through her dancing and writes to express complex concepts into simple words.
Related: Bretton Woods Agreement






